Order now to boost your heating efficiency and equipment performance!
Key Features
-
Rapid Temperature Rise
Made with premium resistance alloys (NiCr, FeCrAl) or ceramic heating cores for quick thermal response and fast reach of set temperatures. -
Uniform Heating
Heating plates use composite lamination technology, and tubular elements are densely arranged to ensure even heat distribution with no hot spots. -
Energy Saving & Eco‑Friendly
Surface treatments such as nitriding or nickel plating boost thermal conductivity and extend service life; efficient insulation design minimizes heat loss. -
High‑Temperature & Corrosion Resistance
Tubes can be made of stainless steel or aluminum alloy; heating plates on ceramic substrates, suitable for –50 °C to +800 °C conditions and various chemical environments. -
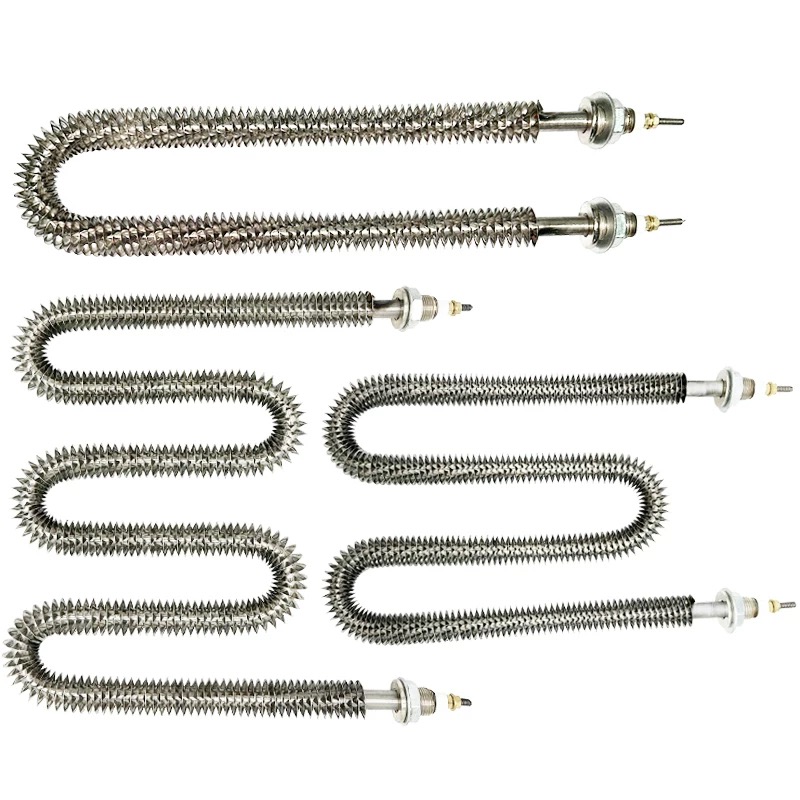
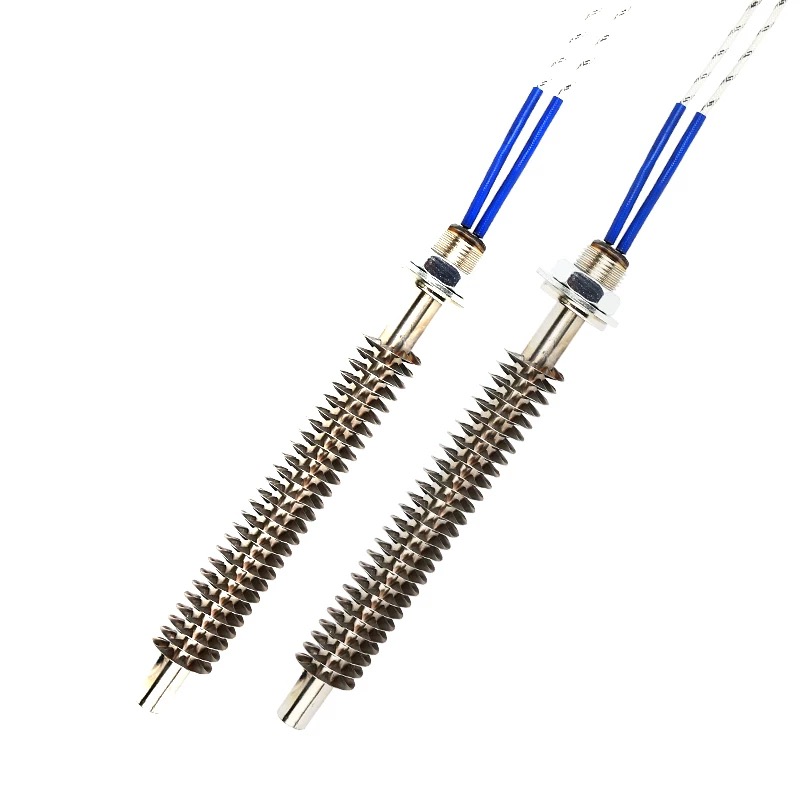
Flexible Installation
Tubular elements support direct‑insertion, flange, threaded, or clamp connections; heating plates can be fixed by adhesive, screws, or embedded into grooves to meet diverse installation needs. -
Customizable Specifications
Power, voltage, length, and thickness are all customizable, and options include single‑phase, three‑phase, and DC power supplies.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Typical Range / Options |
|---|---|
| Power Density | 5 W/cm² – 30 W/cm² (heating plates) |
| Power | 50 W – 10 000 W (tubular elements) |
| Voltage | 12 V / 24 V / 110 V / 220 V / 380 V |
| Operating Temp. | –50 °C to +800 °C |
| Element Size | Tube Ø 6 mm–Ø 25 mm; Plate thickness 0.5–2 mm |
| Connection Types | Flange, threaded, clamp, direct insertion |
| Materials | Stainless Steel 304/316L, Aluminum Alloy, Ceramic Substrate |
| Protection Rating | IP00 – IP67 (depending on housing & cables) |
Typical Applications
-
Air heating (ducts, ovens, dryers)
-
Liquid heating (oil tanks, immersion heaters)
-
Mold heating (injection molds, extrusion molds)
-
Laboratory equipment (incubators, thermostatic chambers)
-
Household appliances (electric kettles, heated blankets)
-
Any application requiring localized or surface heating
Installation & Maintenance
-
Installation
-
Confirm matching of power supply voltage and rating;
-
Ensure tight contact between heating element and workpiece to avoid air gaps;
-
Provide reliable grounding to prevent leakage.
-
-
Commissioning
-
Power up gradually and monitor sensors and controllers for proper response;
-
Adjust power or temperature settings step by step to prevent overshoot.
-
-
Maintenance
-
Regularly inspect terminals, insulation layers, and sealing rings;
-
Clean surface dust and debris to maintain adequate heat dissipation;
-
On fault detection, immediately power down, stop operation, and replace or repair the heating element.
-